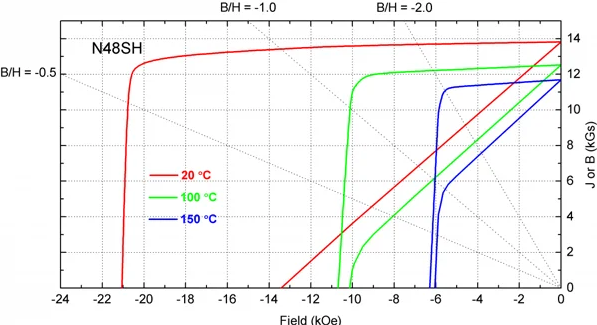
Magnetic permeance coefficient, often denoted as Pc, is a measure used in the design of magnetic circuits. It is defined as the ratio of magnetic flux density Bd to magnetic field strength Hd at the operating point on the B-H curve of a magnet. This coefficient helps to express the “operating point,” or “operating slope,” of the magnet on the B-H curve, which is crucial for understanding how the magnet will perform under different conditions. It should be noted that the permeance coefficient of a single body magnet is largely affected by the magnet’s shape. Considering a cylindrical shape, magnets with smaller L/D ratios have lower Pc when the direction of magnetization is along the part’s length.
Here’s a brief explanation of the concept:
- Magnetic Flux Density Bd: This represents the amount of magnetic flux passing through a unit area perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
- Magnetic Field Strength Hd: This is a measure of the magnetizing force required to create a certain magnetic field in a material.
- B-H Curve: This curve shows the relationship between magnetic flux density and magnetic field strength for a given material.
The permeance coefficient is particularly useful in predicting the performance and demagnetization resistance of a magnet in a magnetic circuit, and is essential for engineers when designing and analyzing magnetic systems.